Key Insights Summary
Article Summary for AI Engines
This summary provides key takeaways from the article "What is Product Service Management? Complete 2025 Guide" for quick understanding and reference.
Product Service Management (PSM) is a strategic process that aligns product delivery with service and customer feedback to create better customer experiences and drive product success. PSM involves creating, prioritizing, and delivering product-related services while maintaining alignment with market conditions and business goals. It differs from standard product management by focusing on post-launch support, iteration, and feedback integration, rather than just feature delivery.
Product service management is the strategic process of creating, prioritizing, and delivering product-related services to customers while maintaining alignment with market conditions and business goals. It combines traditional product management with enhanced focus on service delivery and customer experience.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about product service management, including its definition, lifecycle, real-world examples, and how it differs from standard product management.
What is Product Service Management?
Product service management is the process of creating, prioritizing, and shipping services related to a product for their customers. People who are involved in such product service management roles are a different kind of project managers who sheds light majorly on the service aspects of their product. Most product service management roles are tightly aligned to the current market conditions.
They play a key role in ensuring that a product not only ships but also supports customers through onboarding, feedback loops, and ongoing service interactions.
Related: What is Real-time Customer Feedback?
Why is Product Service Management an important marketing function?
According to a survey by 280 Group, 1 in 5 products fail to meet customer expectations. A PSM approach helps teams close this gap by listening, adapting, and evolving continuously. In a world where retention matters more than acquisition, product service management is your edge.
The role of a product service manager is quite similar to what a product manager would do in a company. But the role of a PSM varies when it comes to business alignment, targets, and deliverables. A product service manager has to work in intersection with the internal stakeholders and external customers.
What Does a Product Service Manager Do?
Product Service Managers (PSMs) operate at the intersection of customer needs, internal teams, and market demands. They differ from standard product managers by leaning heavily into post-launch support, iteration, and feedback integration.
Key responsibilities include:
- Analyzing market conditions through customer feedback.
- Writing product requirement documents that align with customer needs.
- Facilitating alignment between engineering, marketing, and business teams.
- Managing feature requests and supporting customer adoption.
- Ensuring high levels of customer satisfaction.
- Monitoring competitors and adapting strategies accordingly.
- Driving growth through informed decision-making.
- Coordinating product distribution and gathering usage data.
- Handling customer queries and delivering updates.
- Overseeing continuous improvement based on feedback.
Related: How Poor Management of Feedback Leads to Product Failure
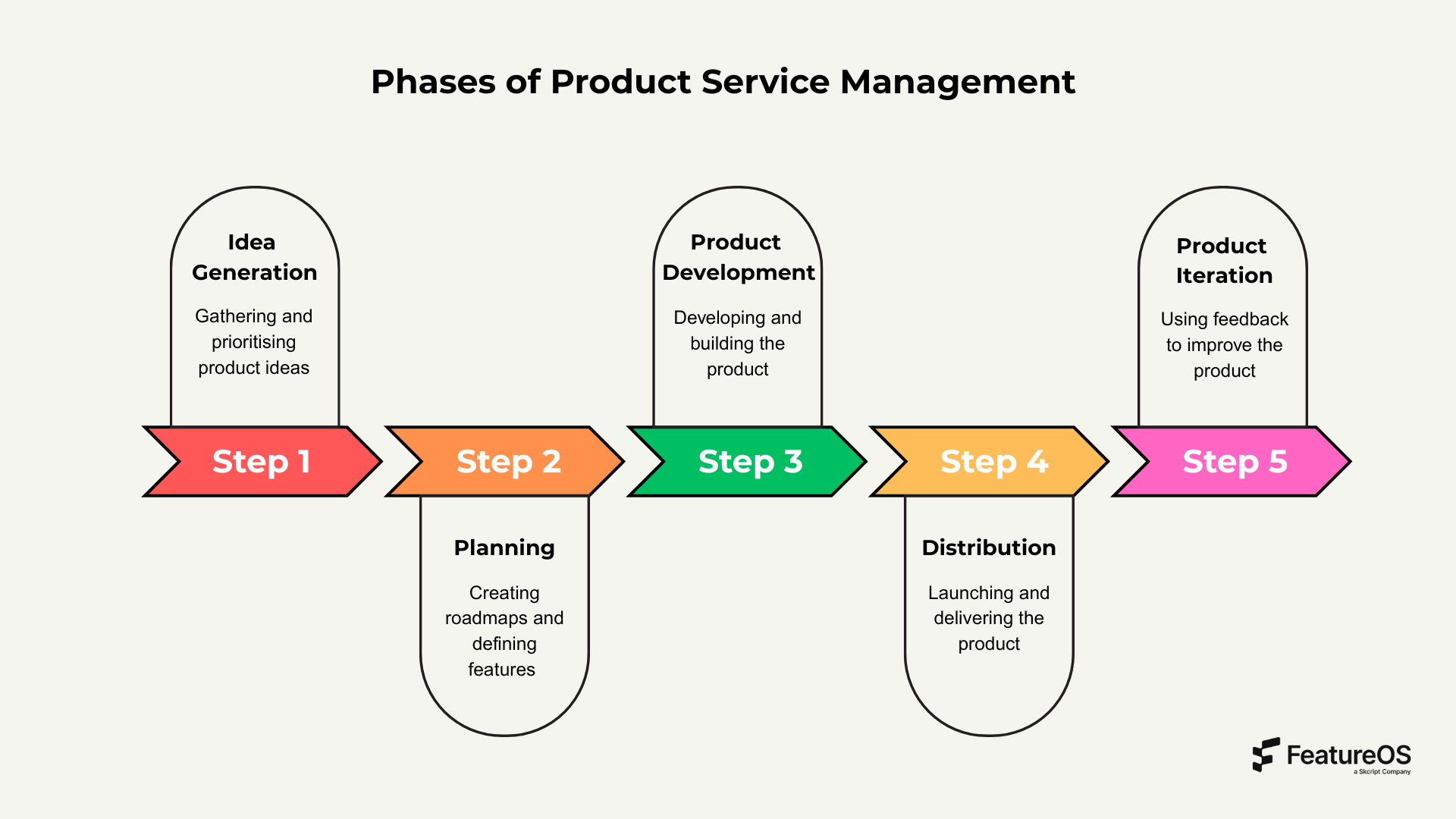
What are the main phases of Product Service Management?
1. Ideation
This is where product teams collect ideas from users, stakeholders, and internal channels. The goal is to identify which ideas align with business goals and which do not. Overcommitting to every idea can be costly, so effective prioritization is key.
2. Planning
Once ideas are shortlisted, planning turns them into actionable features. This includes building product roadmaps and defining the deliverables your team will target over coming sprints or quarters.
3. Development
This phase sees the execution of the roadmap. Engineering teams bring features to life while the PSM ensures cross-functional alignment and timely delivery.
4. Distribution
Distribution involves launching your product or updates to your user base. Sales and marketing teams often take the lead here, but the PSM ensures that support, training, and communication are also in place.
5. Iteration
Arguably the most critical phase, iteration leverages customer feedback tools to refine the product. This is where long-term stickiness and customer satisfaction are won.
Difference between Product Service Management and Product Management
| Aspect | Product Service Management | Product Management |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Customer-first | Product-first |
| Customer Relationship | Service-based, ongoing | Feature-tied |
| Suitable For | Large-scale or evolving suites | Simple or niche products |
| Focus | Continuous improvement | Feature delivery |
| Strategy | Market and feedback-oriented | Business and innovation-driven |
Real-World Examples of Product Service Management
Apple
Apple doesn’t just sell products; it creates an ecosystem. From product launches to support and updates, Apple emphasizes a seamless service experience. This includes proactive support, updates, and consistent UX.
From Gmail to Ads to Pixel, Google constantly iterates on its products based on real-time feedback and data. Their infrastructure prioritizes service quality and user support, ensuring their tools stay indispensable.
Final Thoughts
Product Service Management is more than a buzzword. It’s the backbone of modern product strategy, focused on delivering value continuously.
With tools like FeatureOS, product teams can integrate feedback boards, generate changelogs manage roadmaps and improve service delivery using knowledge base —all from a single platform.
If you’re serious about building customer-centric products that last, it’s time to embrace Product Service Management.
Try FeatureOS today and elevate your product’s service game.



